API Specification 1.1
Components
Desktop Agent
A Desktop Agent is a desktop component (or aggregate of components) that serves as a launcher and message router (broker) for applications in its domain. A Desktop Agent can be connected to one or more App Directories and will use directories for application identity and discovery. Typically, a Desktop Agent will contain the proprietary logic of a given platform, handling functionality like explicit application interop workflows where security, consistency, and implementation requirements are proprietary.
Examples of Desktop Agents include:
- Autobahn
- Finsemble
- OpenFin
- Refinitiv Eikon
Desktop Agents expose an FDC3 standard API to applications they have launched. When an App is launched by a Desktop Agent and is given access to the Agent's API to interoperate, it is running in that Desktop Agent's context.
Desktop Agent Implementation
The FDC3 API specification consists of interfaces. It is expected that each Desktop Agent will implement these interfaces. A typical implemention would provide instantiable classes for the following interfaces:
DesktopAgentChannelListener
Other interfaces defined in the spec are not critical to define as concrete types. Rather, the Desktop Agent should expect to have objects of the interface shape passed into or out of their library. These interfaces include:
ContextAppIntentIntentResolutionAppMetadataIntentMetadataDisplayMetadata
API Access
The FDC3 API can be made available to an application through a number of different methods. In the case of web applications, a Desktop Agent SHOULD provide the FDC3 API via a global accessible as window.fdc3. Implementors MAY additionally make the API available through modules, imports, or other means.
Standards vs. Implementation
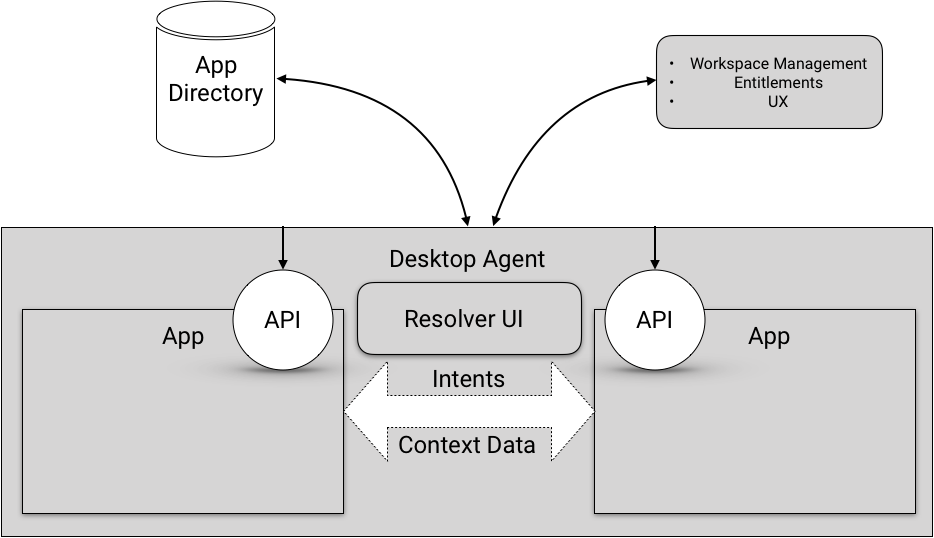
The surface area of FDC3 standardization (shown in white above) itself is quite small in comparison to the extent of a typical desktop agent implementation (in grey).
For example:
- workspace management
- user identity and SSO
- entitlements
- UX of application resolution
Are all areas of functionality that any feature complete desktop agent would implement, but are not currently areas considered for standardization under FDC3.
Inter-Agent Communication
A goal of FDC3 standards is that applications running in different Desktop Agent contexts on the same desktop would be able to interoperate. And that one Desktop Agent context would be able to discover and launch an application in another Desktop Application context.
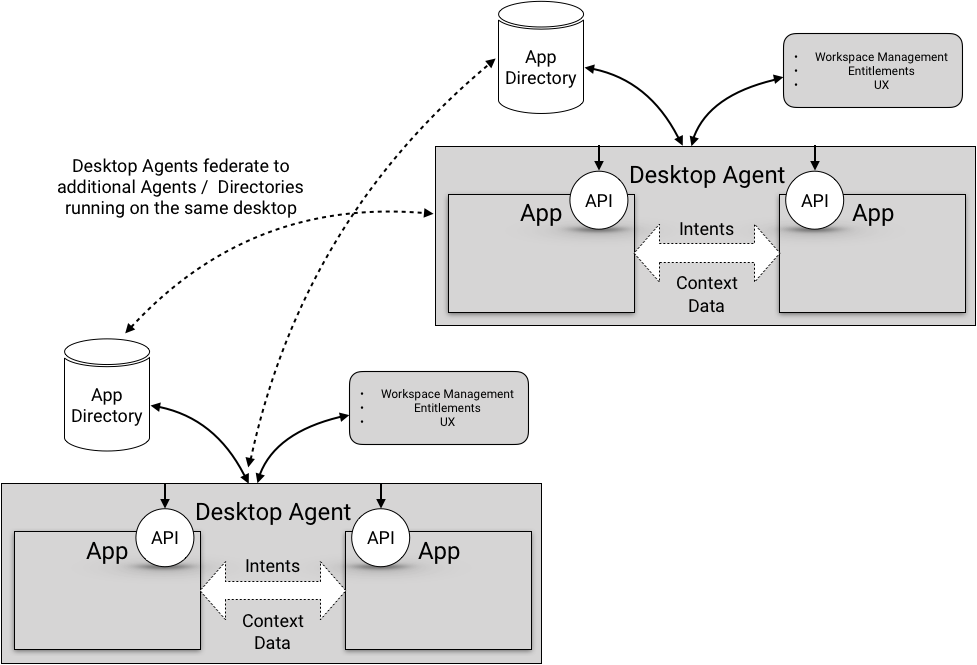
Desktop Agent interop is supported by common standards for APIs for App discovery and launching. So, an App in one Desktop Agent context would not need to know a different syntax to call an App in another Desktop Agent context.
The actual connection protocol between Desktop Agents is not currently in scope for FDC3 standards. Given that there are a relatively small number of Desktop Agents, and that any given desktop will have a finite and relatively static number of Desktop Agents installed at any given time, the connectivity between different Agents can be adequetly handled for the time being on a case-by-case basis.
Application
An application is any endpoint on the desktop that is:
- Registered with/known by a Desktop Agent
- Launchable by a Desktop Agent
- Addressable by a Desktop Agent
Examples of End Points include:
- Native Applications
- PWA/Web Applications
- Headless “services” running on the desktop
Functional Use Cases
Open an Application by Name
Linking from one application to another is a critical basic workflow that the web revolutionized via the hyperlink. Supporting semantic addressing of applications across different technologies and platform domains greatly reduces friction in linking different applications into a single workflow.
Raising Intents
Often, we want to link from one app to another to dynamically create a workflow. Enabling this without requiring prior knowledge between apps is a key goal of FDC3.
Intents provide a way for an app to request functionality from another app and defer the discovery and launching of the destination app to the Desktop Agent. There are multiple models for interop that Intents can support.
- Chain: In this case the workflow is completely handed off from one app to another (similar to linking). Currently, this is the primary focus in FDC3
- Client-Service: A Client invokes a Service via the Intent, the Service performs some function, then passes the workflow back to the Client. Typically, there is a data payload type associated with this intent that is published as the standard contract for the intent.
- Remote API: An app wants to remote an entire API that it owns to another App. In this case, the API for the App cannot be standardized. However, the FDC3 API can address how an App connects to another App in order to get access to a proprietary API.
Intent Resolution
Raising an Intent will return a Promise-type object that will resolve/reject based on a number of factors.
Resolve
- Intent was resolved unambigiously and the recieving app was launched successfully.
- Intent was ambigious, a resolution was chosen by the end user and the chosen application was launched succesfully.
Reject
- An app matching the intent was not found.
- A match was found, but the recieving app failed to launch.
- The intent was ambiguous and the resolver experienced an error.
Resolution Object
If the raising of the intent resolves (or rejects), a standard object will be passed into the resolver function with the following format:
{
source: String;
data?: Object;
version: String;
}
- source = identifier for the Application resolving the intent (null if the intent could not be resolved)
- data = return data structure - if one is provided for the given intent
- version = the version number of the Intents schema being used
For example
try {
const result = await fdc3.raiseIntent('StageOrder');
if (result.data) {
const orderId = result.data.id;
}
}
catch (er){
console.log(er.message);
}
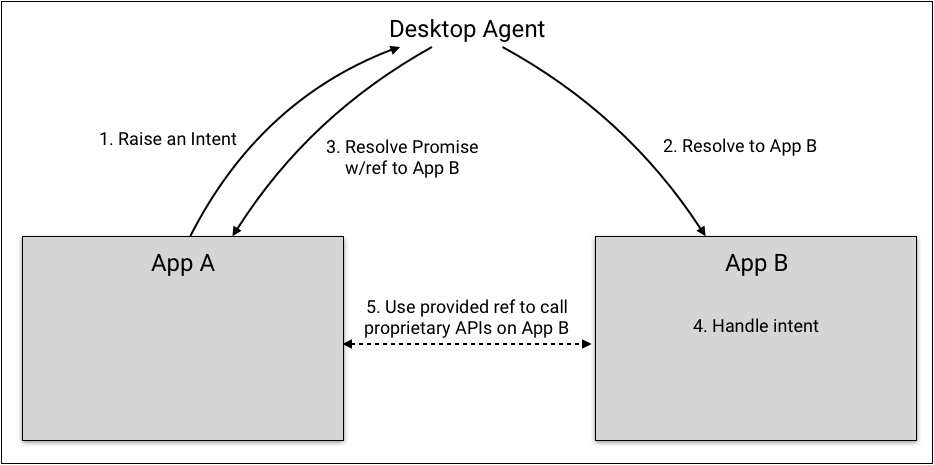
Upgrading to a Remote API Connection
There are a wide range of workflows where decoupled intents and/or context passing do not provide rich enough interactivity and applications are better off exposing proprietary APIs. In these cases, an App can use the source property on the resolution of an intent to connect directly to another App and from there, call remote APIs using the methods available in the Desktop Agent context for the App. For example:
const chart = await fdc3.raiseIntent('ViewChart');
// construct a vendor wrapper for the App
const chartApp = fin.Application.wrap(chart.source);
// do some vendor-specific stuff
Register an Intent
Applications need to let the system know the Intents they can support. Typically, this is done via registration with the App Directory. It is also possible for Intents to be registered at the application level as well to support ad-hoc registration which may be helpful at development time. While, dynamic registration is not part of this specification, a Desktop Agent agent may choose to support any number of registration paths.
Compliance with Intent Standards
Intents represent a contract with expected behavior if an app asserts that it supports the intent. Where this contract is enforceable by schema (for example, return object types), the FDC3 API implementation should enforce compliance and return an error if the interface is not met.
It is expected that App Directories will also curate listed apps and ensure that they are complying with declared intents.
Like FDC3 Context Data, the Intent schemas need to be versioned. Desktop Agents will be responsible to declare which version of the Intent schema they are using. Applications may also assert a specific version requirement when raising an Intent. Version negotation may be supported by a given Desktop Agent.
Send/broadcast context
On the financial desktop, applications often want to broadcast context to any number of applications. Context sharing needs to support concepts of different groupings of applications as well as data privacy concerns. Each Desktop Agent will have its own rules for supporting these features.
Resolvers
Intents functionality is dependent on resolver functionality to map the intent to a specific App. This will often require end-user input. Resolution can either be performed by the Desktop Agent (raising UI to pick the desired App for the intent) or by the app launching the intent - in which case the calling App will handle the resolution itself (using the findIntents API below) and then invoke an explicit Intent object.
Context channels
Context channels allows a set of apps to share a stateful piece of data between them, and be alerted when it changes. Use cases for channels include color linking between applications to automate the sharing of context and topic based pub/sub such as theme.
There are two types of channels, which are functionally identical, but have different visibility and discoverability semantics.
- The 'system' ones, which have a well understood identity. One is called 'global'.
- The 'app' ones, which have a transient identity and need to be revealed
Joining Channels
Apps can join channels. An app can only be joined to one channel at a time. When an app joins a channel it will automatically recieve the current context for that channel.
When an app is joined to a channel, calls to fdc3.broadcast and listeners added through fdc3.addContextListener will be routed to that channel. If an app is not joined to a channel these methods will be no-ops, but apps can still choose to listen and broadcast to specific channels via the methods on the Channel class.
It is possible that a call to join a channel could be rejected. If for example, the desktop agent wanted to implement controls around what data apps can access.
Joining channels in FDC3 is intended to be a behavior initiated by the end user. For example: by color linking or apps being grouped in the same workspace. Most of the time, it is expected that apps will be joined to a channel by mechanisms outside of the app. Always, there SHOULD be a clear UX indicator of what channel an app is joined to.
The 'global' Channel
The 'system' channels include a 'global' channel which serves as the backwards compatible layer with the 'send/broadcast context' behavior in FDC3 1.0. A desktop agent MAY choose to make membership in the 'global' channel the default state for apps on start up.
The 'global' channel should be returned as part of the response from the fdc3.getSystemChannels call. Desktop Agents may want to filter out the 'global' option in their UI for system channel pickers.
Examples
An app queries the current context of the global channel.
const globalChannel = await fdc3.getOrCreateChannel("global");
const context = await globalChannel.getCurrentContext("fdc3.instrument");
An app can explicitly receive context events on the global (or any other) channel, regardless of what it is currently joined to.
// retrieve current fdc3 context
const context = await fdc3.getCurrentContext("fdc3.instrument")
// context is null, as not currently joined to a channel
const globalChannel = await fdc3.getSystemChannels.filter(c => c.id === "global")
const globalContext = await fdc3.getCurrentContext("fdc3.instrument")
// context is instrument AAPL on the global channel
fdc3.joinChannel('global')
const context = await fdc3.getCurrentContext('fdc3.instrument')
// top-level context is now instrument AAPL as well because we have joined the global channel
Direct Listening and Broadcast on Channels
While joining channels automates a lot of the channel behavior for an app, it has the limitation in that an app can belong to only one channel at a time. Listening and Broadcasting to channels using the Channel.addBroadcastListener and the Channel.broadcast APIs provides an app with fine-grained controls for specific channels. This is especially useful for working with dynamic App Channels.
Examples
To find a system channel, one calls
// returns an array of channels
const allChannels = await fdc3.getSystemChannels();
const redChannel = allChannels.find(c => c.id === 'red');
Joining channels
To join a channel. one calls
fdc3.joinChannel(redChannel.id);
Calling fdc3.broadcast will now route context to the joined channel.
App Channels
App channels are topics dynamically created by applications connected via FDC3. For example, an app may create a channel to broadcast to others data or status specific to that app.
To get (or create) a channel reference, then interact with it
const appChannel = await fdc3.getOrCreateChannel('my_custom_channel');
// get the current context of the channel
const current = await appChannel.getCurrentContext();
// add a listener
appChannel.addContextListener(context => {...});
// broadcast to the channel
appChannel.broadcast(context);
APIs
The APIs are defined in TypeScript in src, with documentation generated in the docs folder.