App Directory Discovery
Simple Definition
The App Directory (AppD) is a service that provides a financial application definition that includes a trusted identifier(s) and associated metadata. The information registered as part of an application definition supports discovery, launch configuration, intents and context data supporting the use and interoperability of financial applications.
Topology
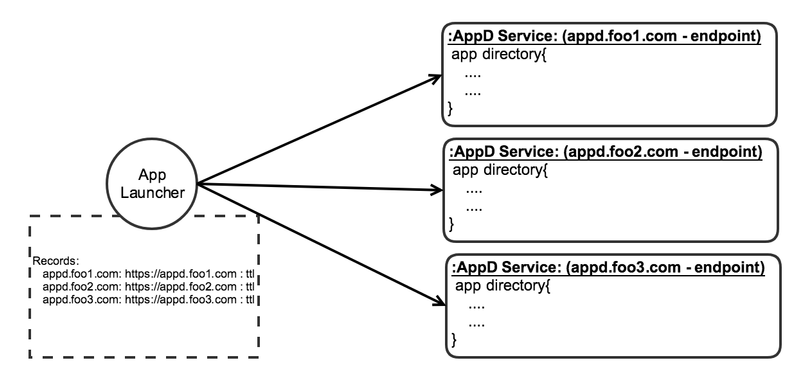
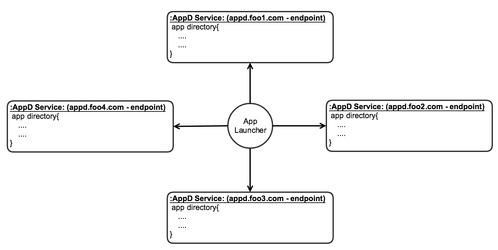
AppD services shall support a distributed or detached model to managing application data servicing, where there are (N) AppD services on a network providing information related to a subset of namespace "zones" that align with the financial application identifiers. This approach encourages independence, scale and responsive provisioning of application definitions. This is modeled from a subset of the public name service "Domain Name System", which has proven reliable and conceptually fit for discovery.
Service Discovery Approach
In order to support the discovery of application data stored in a given directory, name space concepts are introduced to both identify the realm of application definitions and AppD service locations that host data. In simple terms, there has to be a way of discovering the location of the AppD service itself and the associated application definitions that are available from that service.
Application Identifier
- Application data discovery through nested namespace approach and email address construction (name@fqdn) defining the application identifier as the name part and AppD location as the fully qualified domain name part. The entire address should be considered the fully qualified application ID.
Resolving host system
- AppD service host discovery implementations should support the following requirements;
- Discovery of the AppD location using the fully qualified application ID domain name. This would be the fqdn part of the email structure.
- Discovery of the AppD location using the fully qualified application ID domain name to lookup DNS SRV records identifying the host server location and access TCP port. (RFC2782 )
- Statically defined URI records for use within client applications directly. This is similar to #1 above, but provides explicit protocol, port and url definitions as part of the defintion.
Examples:
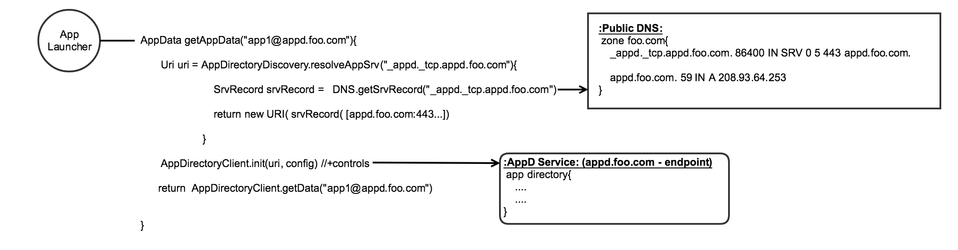
AppD service through DNS / SRV records:
AppD Service distribution visual:
Application data discovery
Application data discovery shall be accessible through a unique application identifier (AppId) representing a single application represented by a nested namespace syntax using dot notation and email address construction (name@fqdn) defining the application identifier as the name part and AppD location as the fully qualified domain name part. The entire address should be considered the fully qualified application ID.
Example:
getAppData("app@sub.root")
Application {
"appId": "app@sub.root",
"name": "App Name",
"manifest": "https://sub.root/app_manifest.json",
"manifestType": "vendor_type",
"version": "1",
"title": "A very cool App",
"tooltip": "A very cool app really",
"description": "Yes..this is the coolest app ever..",
"images": [
{
"url": "string"
}
],
"contactEmail": "string",
"supportEmail": "string",
"publisher": "string",
"icons": [
{
"icon": "string"
}
],
"customConfig": [
{
"name": "string",
"value": "string"
}
],
"intents": [
{
"name": "string",
"displayName": "string",
"contexts": [
"string"
],
"customConfig": {}
}
]
}
Service Discovery (Expanded)
The following represents the three ways AppD service instances should be discovered over a given network. Again, the view is that AppD services are distributed/decoupled based on associated application namespace on a given network. This takes into account the use of the application identifiers described in previous section. A launcher is required to use a URI (e.g. "https://appd.foo.com/api/appd/app1@appd.foo.com") to query a given directory instance for data. In order to construct a URI, the host location and port of a given AppD service instance is required. This proposal focuses on the following approaches to achieve this resolution.
Application ID namespace syntax host resolution
An application directory URI can be constructed using a fully qualified application ID (email address syntax) by using fqdn part of the ID as the host location and the name part as the application name. Given an application name "app1" with a fully qualified identifier of "app1@appd.foo.com" an application directory host location can be derived by simply extracting the fqdn "appd.foo.com" from the email syntax. The extracted fqdn "app.foo.com" may resolve to the actual host location where the application directory is running.
A launcher can then easily construct a URI by;
- URI protocol is defaulted to https, but can be overridden by the launcher.
- URI hostname is the fully qualified domain of the application ID.
- URI port is default https/443, but can be overridden by the launcher
- URI url is by default "/api/(service)/(version)" . It is recommended that we identify service label as "appd" with version being optional. Calls that are made without version automatically default to latest "/api/appd/app1" vs "/api/appd/v1/app1"
The resulting URI to retrieve application data for "app1" would be "https://appd.foo.com/api/appd/v1/app1@appd.foo.com"
Application identifiers, Shrinking the URI and AppdD defaults
Although the concept of fully qualified application IDs are useful in resolving the actual host of the application directory, there is no requirement for an application directory to use this fully qualified application ID as the resolver for a record. An application ID is unique to given application directory, but there is no requirement to use the fully qualified representation when querying an interface. Taking the prior example, the fully qualified application ID "app1@appd.foo.com" is represented as "app1" within the application directory. As a result a launcher can use a shortened URI construct "https://appd.foo.com/api/appd/v1/app1" to resolve the application data vs "https://appd.foo.com/api/appd/v1/app1@appd.foo.com".
DNS/SRV Records
Another approach to support AppD service discovery (resolution) is through use of existing domain name service (DNS) implementations that are broadly used on the Internet today (see: RFCs). Name service implementations can be considered critical infrastructure and are proven stable with over twenty years of use. Name services can be used both through public Internet or locally deployed intranet, which provides optionality to deployment schemes.
More specifically, resolution of an AppD service instance (host location) can be implemented using DNS "service records" (SRV) providing the host instance, protocol and associated port. The following is a well known description of a SRV record (RFC2782):
zone name { _service._proto.name. TTL class SRV priority weight port target.}
- service: the symbolic name of the desired service. For AppD service, this must be identified as "_appd"
- proto: the transport protocol of the desired service; this is usually either TCP or UDP. For AppD service _tcp must be used.
- name: the domain name for which this record is valid, ending in a dot. For AppD service, the name should directly map to the application identifier domain.
- TTL: standard DNS time to live field.
- class: standard DNS class field (this is always IN).
- priority: the priority of the target host, lower value means more preferred.
- weight: A relative weight for records with the same priority, higher value means more preferred.
- port: the TCP or UDP port on which the service is to be found. For AppD service, TCP should always be used.
- target: the canonical hostname of the machine providing the service, ending in a dot. This would be the host where the AppD service is running.
For AppD Service the SRV record must use the following definitions:
- service = _appd
- proto = _tcp
- name = must map to the domain of the application identifier . Example: the name for application identifier "app1.appd.foo.com" would be "appd.foo.com"
Known domains:
Although SRV records provide the means of resolving the location of an AppD service for a specific domain, there could be a need to know what domains exist in the universe. This would be a list of domains representing all known directory instances. It is recommended that the FDC3/FINOS organization publish a list of known domains which support AppD services. This publication can be handled in multiple ways, such as structured files or API endpoints. This proposal shall not provide a qualified solution to achieve this, but rather draw attention to a potential requirement.
Static configuration
As the name implies, a static configuration for the AppD service location is predefined within the launcher following the same domain:URI model mentioned in previous sections.